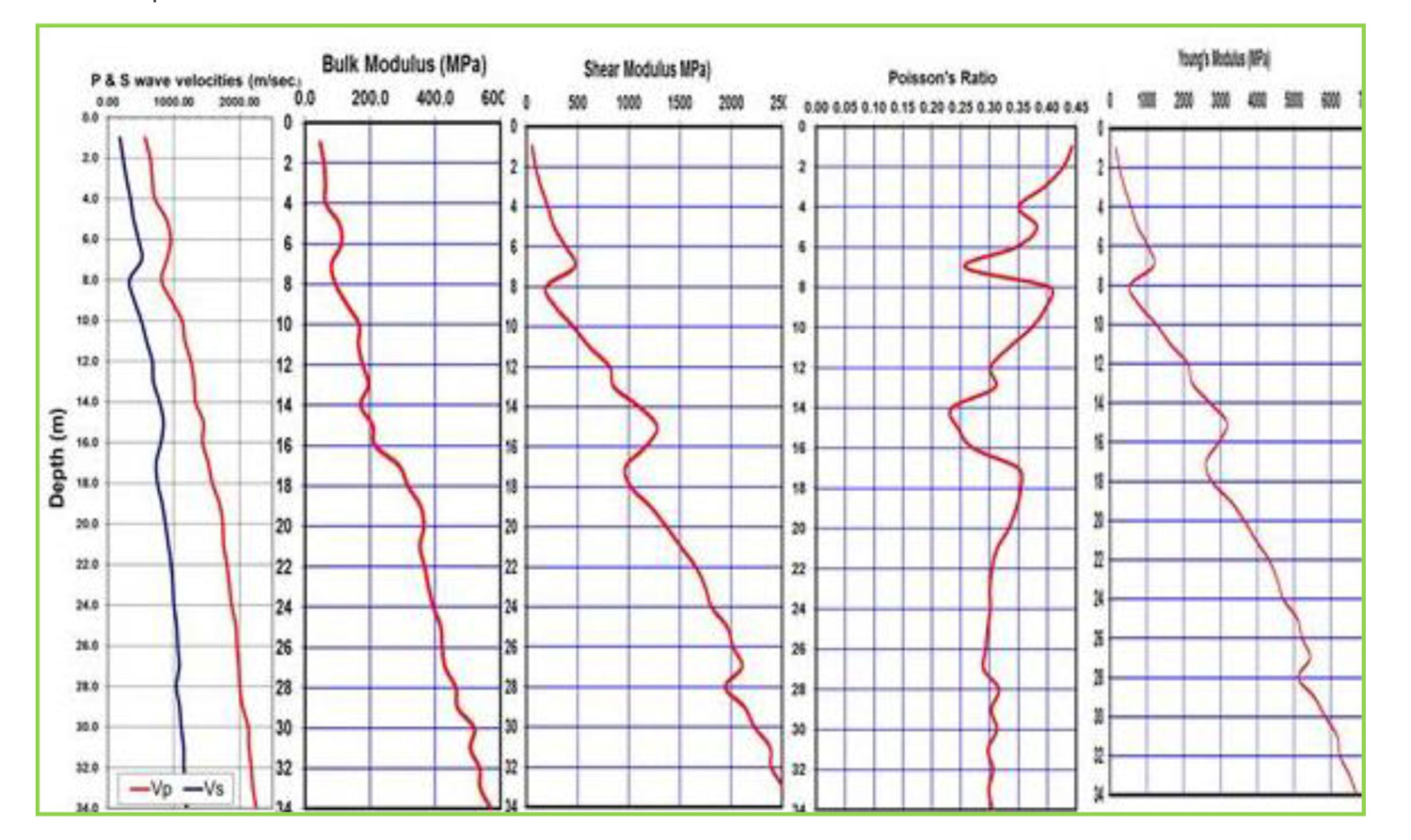
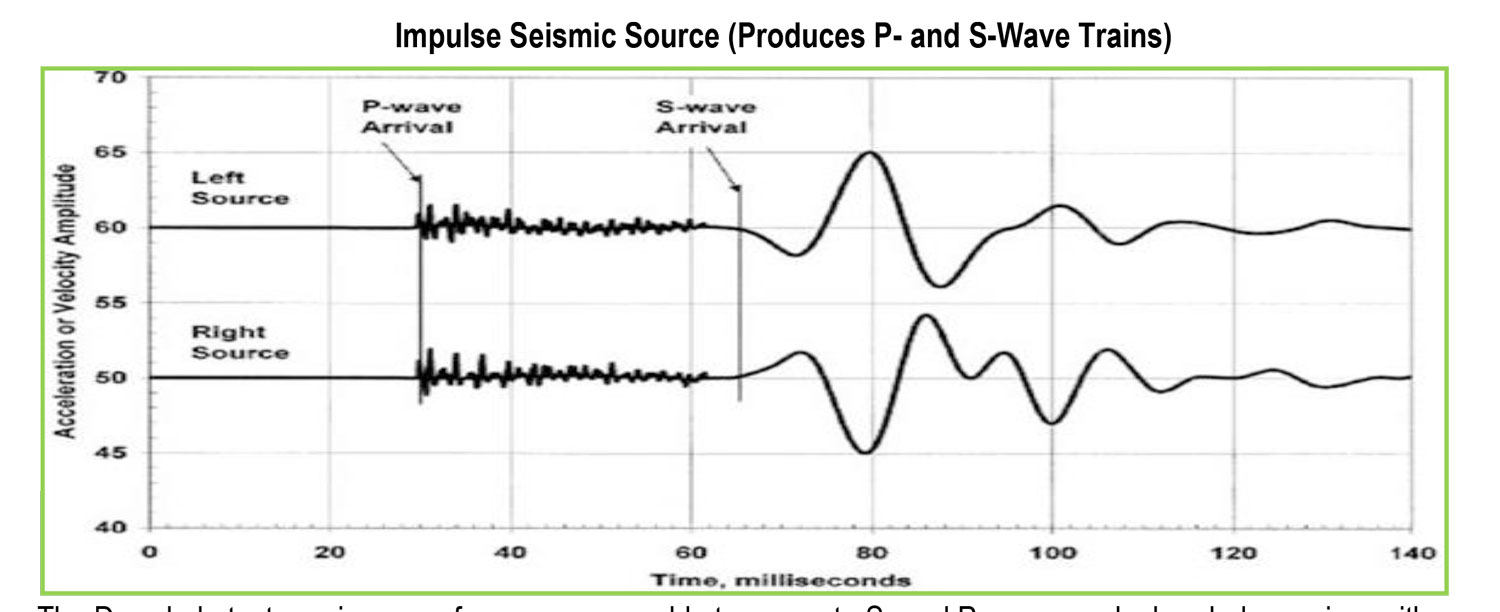
The seismic Downhole method provides a designer with information pertinent to the seismic wave velocities of the materials). The P-wave and S-wave velocities are directly related to the important geotechnical elastic constants of Poisson’s ratio, shear modulus, bulk modulus, and Young’s modulus. Accurate in-situ P-wave and S-wave velocity profiles are essential in geotechnical foundation designs. These parameters are used in both analyses of soil behaviour under both static and dynamic loads where the elastic constants are input variables into the models defining the different states of deformations such as elastic, elastic-plastic, and failure. Another important use of estimated shear wave velocities in geotechnical design is in the liquefaction assessment of soils. The Downhole Test is a method which determines soil stiffness properties by analysing direct compressional and shear waves along a borehole down to about 30 m. The aim of the downhole testing is to derive elastic rock properties such as Poisson’s ratio or Young’s modulus. Shear waves have to be generated at surface. A shear wave source (sledge hammer hit sidewise) is used at surface and a coupled receiver system is moved in the borehole. Travel times of the seismic waves are analysed and seismic velocity is calculated. Shear wave velocity can be transformed to soil stiffness. The measurements can be performed below and above the groundwater table. A grouted casing (e.g. PVC) with a diameter between 3 and 3.45 inch needs to be prepared.