Ground probing radar also known as ground penetration radar (GPR) is a high resolution, field-portable geophysical method that produces graphic sections of subsurface structure. Typical site investigation applications include the accurate location of voids and buried obstructions; mapping subsurface soil and rock interfaces and defining buried archaeological structures. Ground probing radar can also identify ancient landfill sites and detect buried hazardous waste. Ground radar surveys are non-destructive and non-intrusive, revealing detailed information on subsurface ground conditions and can be used for the targeting of expensive drilling operations. On sensitive sites where intrusive investigations are not permissible, a ground radar survey will provide valuable information about the site. Survey results are presented in an easy to understand engineering compatible CAD format. Exploration depth can be limited by soil or water with high conductivity. Detectability depends upon a dielectric contrast between the subsurface feature and the surrounding material.
Applications:
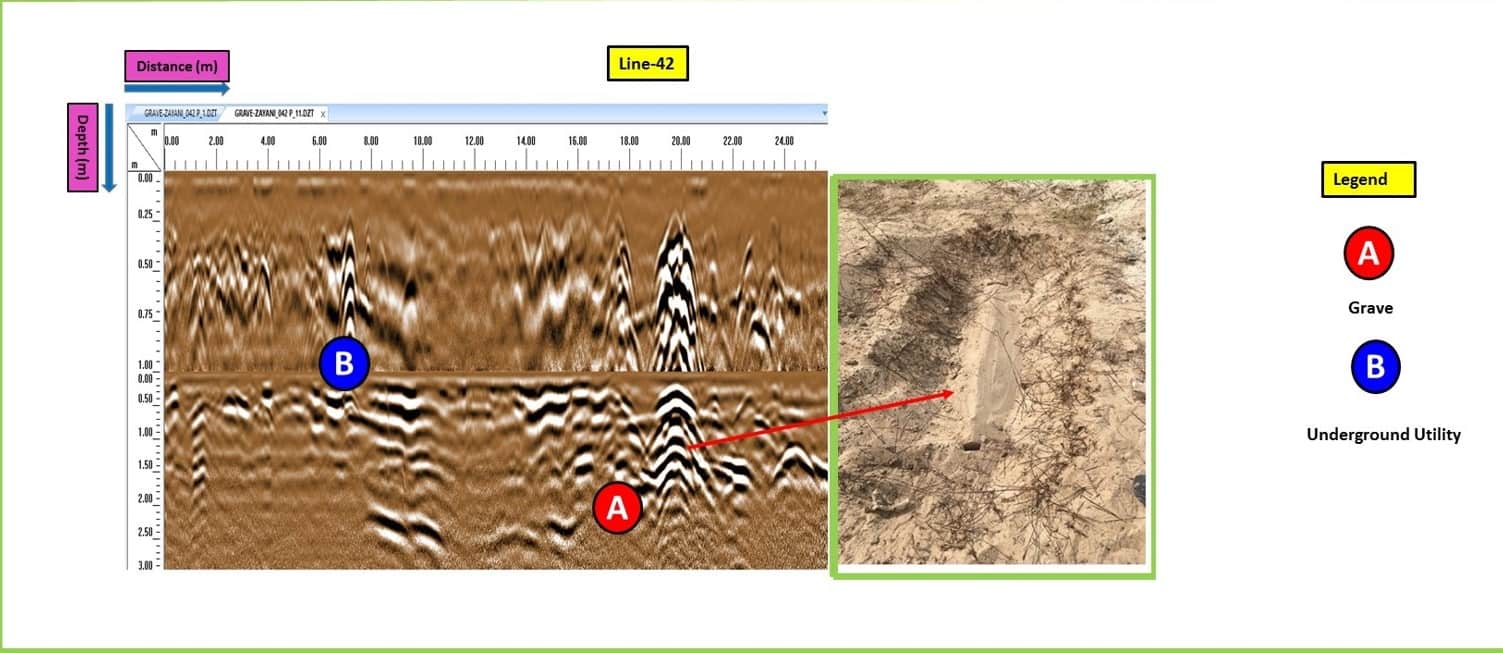
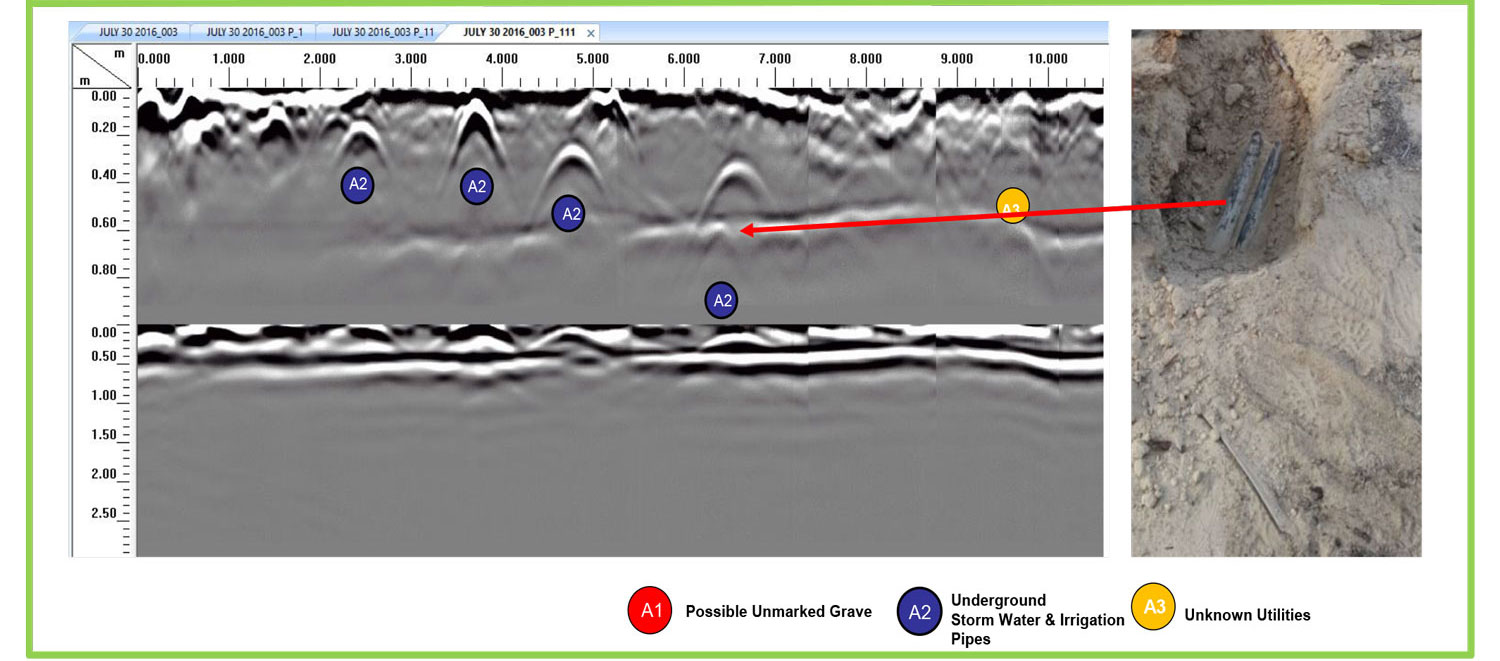
Detects buried voids & cavities, archaeology, unmarked graves
Determines depth of bedrock and overburden thickness
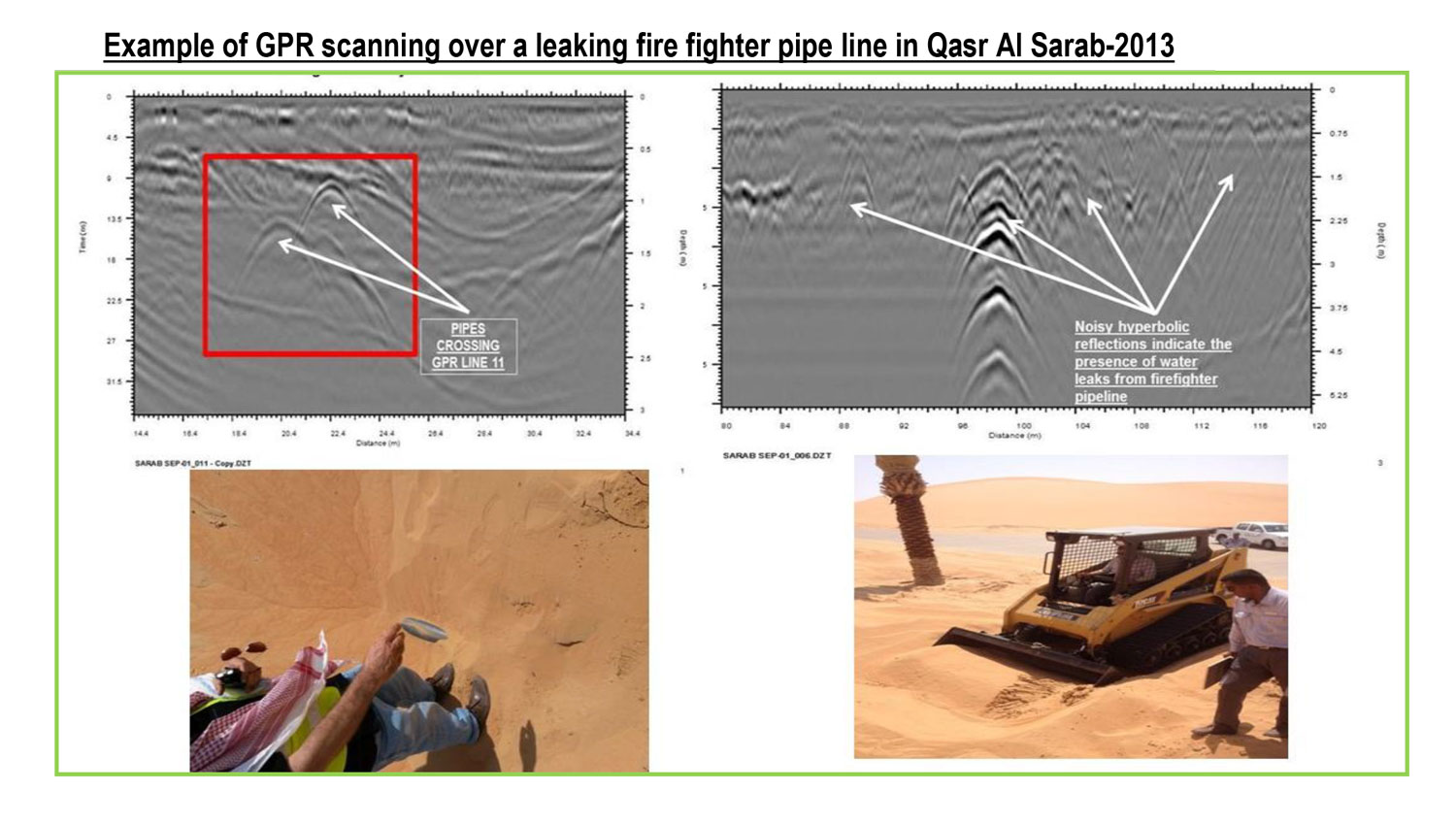
Finds buried underground storage tanks (USTs) and drums
Locates buried foundations and other obstructions
Maps boundaries of closed landfills
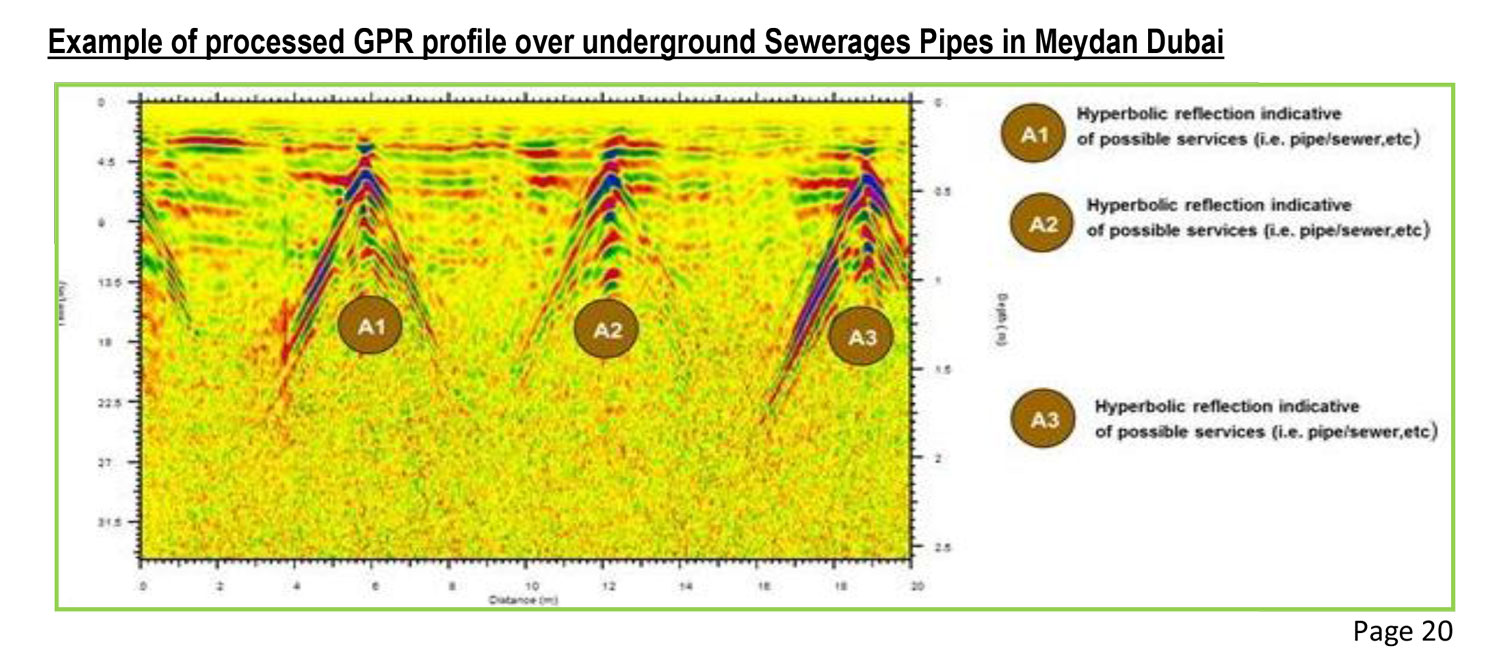
Tracks non-metallic sewer lines
Defines position of pits, ditches and graves